What is Catalog Management?
In sales, a “catalog” means a carefully chosen collection of products that you can buy. To accelerate product sales, sales teams, retailers, and other distribution partners need access to the latest product information, pricing details, and digital assets for every item in the catalog. Catalogs are like organized lists of items, grouped together for various reasons. Catalog management is the process of creating, organizing, updating, and maintaining a catalog of products or services that a business offers. It is an important aspect of retail, e-commerce, and many other industries where businesses need to showcase and sell products and services to customers. Effective catalog management helps businesses efficiently present their offerings, streamline operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Maintaining accurate and consistent product information across various sales channels is a challenge for businesses, particularly those with complex supply chains and extensive product catalogs. Implementing a Product Information Management (PIM) system allows businesses to efficiently oversee and maintain a single, authoritative source of up-to-date information for all of their products.
Catalog management using a PIM system also introduces a framework for overseeing and assigning responsibility for product listing data. By ensuring that individuals with the appropriate permissions and roles are responsible for managing product information, businesses can quickly deliver precise product details to customers. This, in turn, leads to increased sales and enhanced customer loyalty.
Key Components
Product Information: Detailed and accurate information is the foundation of any catalog. This includes product names, descriptions, prices, SKUs (Stock Keeping Units), and other essential details.
Categorization: Products should be categorized logically, making it easier for customers to navigate the catalog. Categories and sub-categories help users find what they’re looking for.
Inventory Management: Keeping track of product availability and stock levels is crucial for fulfilling customer orders and preventing operational disruptions.
Pricing and Discounts: Managing product pricing, including regular prices, sales prices, discounts, and promotions, is essential for both customers and revenue.
Product Variations: Many products come in different sizes, colors, or configurations. Managing these variations and ensuring customers can select the specific product they desire is part of catalog management.
Digital Assets: Multimedia assets, such as images, videos, and 3D models, are essential for showcasing products. Managing these assets and keeping them up-to-date is an important component.
Product Reviews and Ratings: Allowing customers to leave reviews and ratings for products is a common feature of e-commerce platforms. Monitoring and moderating these reviews to maintain a positive reputation is part of catalog management.
Cross-selling and Upselling: Suggesting related or complementary products to customers can boost sales. Catalog management involves setting up these suggestions based on customer behavior and preferences.
Integration: Catalogs must often be integrated with various systems, including e-commerce platforms, inventory management, and CRM software. This integration ensures seamless data flow and real-time updates.
Localization: For businesses operating in multiple regions or countries, catalog management involves creating localized versions of the catalog to cater to different markets with language and cultural differences.
Visual Overview of Catalog Management Components
This visual representation offers a simple yet informative overview of the interconnected nature of catalog management.
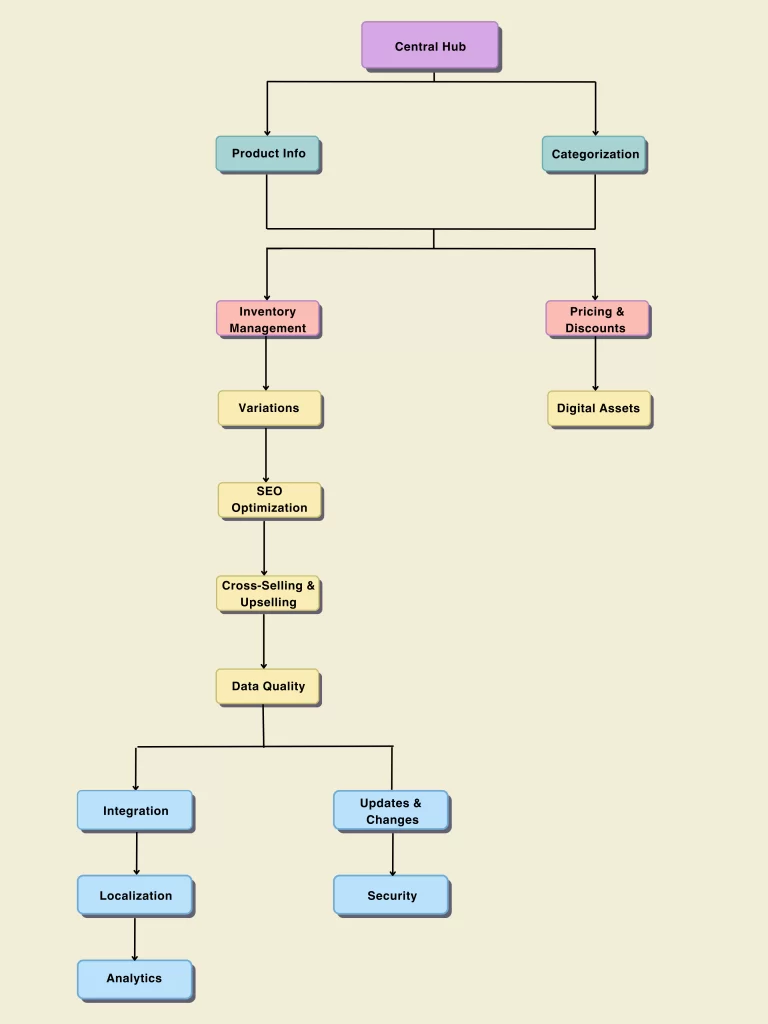
Central Hub: Core of catalog management.
Product Information: Essential product details.
Categorization: Organizing products details
Inventory Management: Monitoring stock levels.
Pricing and Discounts: Managing pricing effectively.
Digital Assets: Multimedia for product showcasing.
Product Variations: Handling different options.
SEO Optimization: Improving search visibility.
Cross-selling & Upselling: Boosting sales with suggestions.
Data Quality: Ensuring accurate and consistent data.
Integration: Seamless data flow with other systems.
Updates & Changes: Keeping the catalog current.
Localization: Adapting for diverse markets.
Security: Protecting data from threats.
Analytics: Gaining insights for improvements.
Importance
Enhanced Customer Experience: A well-organized catalog makes it easier for customers to browse and find products, leading to a more positive shopping experience. It reduces frustration and increases the chances of conversions.
Increases Efficiency: Catalog management streamlines internal operations. It ensures that product information is consistent, accurate, and readily available to various teams within the organization, such as marketing, sales, and customer support.
Increased Sales: Properly managed catalog leads to higher sales. This includes showcasing products effectively, offering appropriate cross-selling and upselling suggestions, and optimizing outcomes for search engines.
Inventory Control: managing product information, including stock levels and availability, is important for inventory control. This prevents overstocking, stockouts, and associated financial losses.
Controls Product Information: Accurate and up-to-date product information is essential for any business. Catalog management ensures that product details, including descriptions, specifications, pricing, and availability are consistent and reliable. It helps prevent errors, such as displaying incorrect prices or product descriptions, which leads to customer dissatisfaction and potential legal issues.
Standardize Multiple Systems: Many businesses operate across various sales channels and platforms, including e-commerce websites, mobile apps, brick-and-mortar stores, and more. Catalog management standardizes product data across these diverse systems. It ensures that product information remains consistent and synchronized across all channels, preventing discrepancies that might confuse customers.
Organizes Product Data Across Devices and Networks: In today’s multi-device and multi-channel world, customers access product information through smartphones, tablets, desktops, and more. Catalog management organizes product data to be accessible and consistent across all these devices and networks. This organization of product data increases customer experiences and makes it easy for customers to find what they need, regardless of the devices they use.
Presents Your Offering More Effectively: A well-managed catalog is a powerful marketing tool. It enables businesses to showcase their products and services effectively. Through proper categorization, attractive imagery, clear product descriptions, and integrated SEO strategies, catalog management ensures that your offerings are presented in the most appealing and persuasive way to potential customers.
Catalog Management Software Types
Product Information Management (PIM) Software: PIM software is designed to centralize and manage detailed product information. It focuses on data quality, enrichment, and consistency.
Examples:
- Akeneo: Popular open-source PIM solution.
- inRiver: Cloud-based PIM platform known for its flexibility.
- Salsify: PIM solution that digital asset management (DAM) and syndication features.
Inventory Management Software: It is made to track and control stock levels, order management, and replenishment.
Examples:
- TradeGecko (now QuickBooks Commerce): Cloud-based inventory management solution with order management features.
- Zoho Inventory: Part of the Zoho suite, this software offers inventory control and order tracking.
- Fishbowl: It provides inventory management and manufacturing solutions for small and midsize businesses.
Digital Asset Management (DAM) Software: It is sussed for organizing, storing, and distributing digital assets, such as images, videos, and documents.
Examples:
- Adobe Experience Management (AEM): Adobe’s DAM system includes image and video management features.
- Widen Collective: Widen offers DAM solutions for creative and marketing teams.
- Bynder: It is a cloud-based DAM platform designed for brand management.
E-Commerce Platform Catalog Management: E-commerce platforms often have built-in catalog management features that help users create and manage product listings.
Examples:
- Shopify: It offers a robust catalog management system with e-commerce capabilities.
- WooCommerce (for WordPress): A popular WordPress plugin that adds e-commerce and catalog management functionality.
- Magento: It is a flexible open-source e-commerce platform with complete catalog management.
Supplier Portal Software: It allows businesses to collaborate with suppliers, share product information, and manage catalogs together.
Examples:
- JAGGAER: JAGGAER’s supplier management solutions enable collaboration and catalog updates with suppliers.
- SAP Ariba: SAP Ariba offers procurement solutions that include supplier collaboration and catalog management.
On-Premise Catalog Management Software: It is installed and maintained on your organization’s own servers and infrastructure, You have complete control over the software and data. It can often be customized to meet your specific needs and integrate with other in-house systems.
Examples:
- SAP Master Data Governance: SAP offers on-premise catalog management solutions as part of its Master Data Governance Suite.
- Informatica MDM: Informatica provides on-premise MDM solutions that include catalog management features.
Open-Source Catalog Management Software: It is available to the public for free or with minimal cost. It provides the source code, allowing users to modify and customize the software to their specific needs. Open-source solutions are often budget-friendly as there are no licensing fees.
Examples:
- Akeneo (Community Edition): Akeneo offers an open-source version of their PIM software, known as the Community Edition.
- Magento (Open Source): Magento provides an open-source e-commerce platform with catalog management features.
SaaS Catalog Management Software: It is hosted in the cloud, and users access it via the internet. It is managed and maintained by the software provider. SaaS solutions often have a subscription-based pricing model, reducing upfront expenses.
Examples:
- Wix Stores: Wix offers a SaaS-based e-commerce platform with catalog management features.
- Plytix: Plytix provides a cloud-based PIM platform with SaaS deployment.