What is Adobe Commerce?
Adobe Commerce, which is also known as Magento, is a commerce platform that’s designed to be flexible and scalable. This means it can adapt to the needs of different businesses and grow with them over time.
One of the standout features of Adobe Commerce is its ability to create personalized customer experiences. Whether your business is B2B (business-to-business) or B2C (business-to-consumer), Adobe Commerce can help you tailor your online presence to serve your customers better.
Adobe Commerce is built using PHP and uses MySQL or MariaDB for its relational database management system. This means it’s built on widely used technologies that many developers are familiar with.
Finally, Adobe Commerce supports a range of commerce types, including business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), omnichannel commerce, and mobile commerce. This makes it a versatile choice for businesses operating in different sectors or markets.
Key Features
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento Commerce, is a powerful e-commerce platform that offers a wide range of features for businesses of all sizes. Here are some key features:
B2C and B2B Shopping Experiences: Adobe Commerce supports Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Business-to-Business (B2B) models. This means it can handle transactions between businesses, as well as transactions between businesses and individual consumers. It provides a rich set of features out-of-the-box to create a world-class shopping experience.
Ecosystem and Customization: Adobe Commerce has a global ecosystem of implementation partners and a vast marketplace of extensions. This means you can find pre-built modules and themes to extend the functionality of your store. It also supports third-party integrations, allowing you to connect your store with other business systems.
Flexibility and Customisation: Adobe Commerce is highly customizable, giving you complete control over the design, functionality, and content of your online store. This means you can tailor your store to fit your brand and meet your specific business needs.
Inventory Management: Adobe Commerce includes features for managing your product inventory. This can help you keep track of stock levels, manage suppliers, and ensure you always have enough products to meet customer demand.
Order Tracking: Adobe Commerce provides integrated checkout, payment, and shipping solutions. This means customers can easily make purchases, and you can track orders from placement through delivery.
Content Management System (CMS): Adobe Commerce includes a robust content management system. This allows you to easily manage and update the content on your site, such as product descriptions, blog posts, and more.
Scalability and SEO-friendliness: Adobe Commerce is designed to scale with your business, so it can handle increased traffic and sales as your business grows. It’s also SEO-friendly, meaning it includes features to help improve your site’s visibility in search engine results.
Advanced Marketing and Merchandising Capabilities: For larger businesses with more complex needs, Adobe Commerce offers advanced marketing and merchandising capabilities. This includes features for customer segmentation, content staging, and more.
24/7 Customer Support: Adobe Commerce provides round-the-clock customer support. This means you can get help when you need it, whether you’re having technical issues or need assistance with implementation and ongoing management.
Benefits of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, powered by Magento, offers several benefits for both B2B and B2C shopping experiences:
Scale and Extensibility: Adobe Commerce is designed to handle the growth of your business. It can manage large orders and unlimited growth. It is easy to incorporate new technology, create new storefronts, and deploy shopping experiences across any device or channel. This is possible due to its cloud-based, headless architecture and tools like Adobe Developer App Builder, making it easy to scale and integrate commerce experiences across all digital touchpoints. It also allows for quick integration of new brands and product catalogs, deployment of multi-tenant, multi-region storefronts, and creation of multichannel connected experiences.
Multi-Channel Commerce: Adobe Commerce allows you to manage multiple channels, brands, and sites – including B2B and B2C hybrid commerce – from a single back end. It provides a unified back end that allows you to easily manage a growing product catalog, large orders, and traffic spikes. This means you can manage all aspects of your business, such as product catalog, customized price lists, brands, sites, sales channels, and countries you do business in, from one central location.
Personalized Commerce: Adobe Commerce uses AI-powered features like Live Search and Product Recommendations to personalize both B2C and B2B buying journeys. This helps deliver more relevant and personalized shopping experiences, improving conversion, retention, cross sales, and up sales.
Operational Confidence: Adobe Commerce provides enterprise-level security and can host thousands of SKUs. It automatically scales to meet high traffic demands. It simplifies workflows, reduces the total cost of ownership, and accelerates time to value through native integrations and AI. It also provides a secure, cloud-native infrastructure that supports high traffic, steady performance, and responsive customer experiences.
Platform Architecture: Adobe Commerce provides an adaptable, headless solution to help you create inventive commerce journeys. Its modular, open architecture gives developers control over every aspect of the application and the ability to extend Adobe Commerce capabilities in a serverless, scalable environment.
AI-Driven Intelligent Commerce: Adobe Commerce uses AI to deliver relevant and personalized experiences. It uses your database along with your other systems to provide insights that accelerate smart, data-driven decisions.
Future-Proof Scalability and Extensibility: Adobe Commerce is built to grow as you do. It makes it easy to incorporate new technology, spin up new storefronts, and deploy app-like shopping experiences across any device or channel. This can help ensure your e-commerce platform remains relevant and effective as technology and customer expectations evolve.
In summary, Adobe Commerce is a robust platform that offers a wide range of features and capabilities to help businesses create a compelling eCommerce site with a powerful user experience. It also offers the benefits of modern cloud computing, built on a cloud-native and extensible architecture.
Drawbacks of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento, is a robust e-commerce platform. However, it does have some drawbacks:
Complexity: Adobe Commerce is a feature-rich platform, which means it has a lot of options for customization. This can be overwhelming for beginners who are not familiar with such a comprehensive platform. It requires time and effort to understand how to effectively use all the features.
Cost: Adobe Commerce can be quite expensive, especially for small businesses. The cost is based on the gross sales revenue of a company. For companies with high sales volumes, the cost can easily reach $100,000 per year. Even setting up a basic online store on the Magento Open Source edition can cost up to $5,000, while a large Adobe Commerce Cloud store will cost up to $200,000.
Requires Development Skills: Adobe Commerce is not very user-friendly for non-developers. It requires a good understanding of Adobe Commerce admin development, architecture, EAV/database, layout/UI, checkout and sales, and catalog. Familiarity with Adobe Commerce – version 2.4 and a good understanding of PHP is also necessary.
Performance: While Adobe Commerce is designed to handle large and complex catalogs, high transaction volumes, and global regions, it requires robust hosting solutions for optimal performance. Without proper hosting, the platform can slow down. In a performance benchmark test for Adobe Commerce on Cloud version 2.4.5, it was found that with Adobe Commerce’s capability to horizontally scale both web and database tiers, customers can scale beyond the number shown: 208,000 orders per hour, 2 million pageviews per hour, 242 million effective SKUs, 10,500 GraphQL calls per minute, 500 concurrent back-office users.
Pricey Themes: The themes for Adobe Commerce can be quite expensive. Engaging and artistic themes can range from $17 to $399. For customized themes, the cost can go up to $5,000 or more.
Reasons to Choose Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento, is a top choice for many businesses due to its robust features and capabilities. Here are some reasons why businesses choose Adobe Commerce:
Enterprise-Level Tools: Adobe Commerce provides a suite of tools that are typically used by large businesses. These tools can help in creating and managing a powerful online store, including inventory management, customer service, and more.
Omnichannel Shopping Experiences: Adobe Commerce allows businesses to provide a seamless shopping experience across multiple channels (like online, in-store, mobile, etc.). This means customers can shop from anywhere, anytime, and on any device.
Scalability: As your business grows, Adobe Commerce can scale with it. It offers more features and capabilities as your business needs to expand. This means it can handle increased traffic, more products, and more customers as your business grows.
B2B and B2C Transactions: Adobe Commerce supports both B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Consumer) transactions. This means it can handle sales directly to consumers as well as transactions between businesses.
Analytics and Marketing Tools: Being part of Adobe’s suite, Adobe Commerce comes with advanced analytics and marketing tools. These tools can help businesses understand their customers better and create effective marketing campaigns.
Customization Options: Because Adobe Commerce is open-source, it offers extensive customization options. Businesses can modify the platform to suit their specific needs and preferences.
Integration Capabilities: Adobe Commerce can be integrated with other applications, which can enhance business efficiency. This means it can work seamlessly with your existing business systems, like your CRM or ERP.
Differentials of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento Commerce, offers several key differentials that make it a popular choice for businesses:
Cloud-Based Architecture: Adobe Commerce is built on a cloud-native and extensible architecture. This means it is designed to leverage the benefits of cloud computing, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It offers two plans: Starter and Pro, each with unique architecture to drive your Adobe Commerce development and deployment process. Both plans deploy databases, web servers, and caching servers across multiple environments for end-to-end testing while supporting continuous integration. This cloud-based structure provides substantial advantages for internal teams and digital customer experiences.
Scalability and Performance: Adobe Commerce is designed to meet the demands of mid-size and enterprise businesses, supporting large and complex catalogs, high transaction volumes, and global regions. It can handle 208,000 orders per hour, 2 million pageviews per hour, 242 million effective SKUs, 10,500 GraphQL calls per minute, and 500 concurrent back-office users. This is achieved through its capability to horizontally scale both web and database tiers, managing it can add more servers to handle increased load.
Auto Scaling: Adobe Commerce offers horizontal auto-scaling on the web tier for customers on scaled architecture. This feature ensures stable performance during unplanned traffic spiked by automatically adding resources. An auto-scaling event occurs when CPU usage and traffic reach a predefined threshold, allowing the system to respond to changes in demand.
Reliability and Monitoring: The Adobe Commerce infrastructure is built to support high traffic, maintain steady performance, and offer consistently responsive shopping experiences. Customers get access to New Relic and security monitoring tools included with their Adobe Commerce license. These monitoring tools provide merchants and developers with full visibility into the overall health, performance, and security of the platform’s architecture and application.
Integration with Adobe Experience Manager, Adobe Target, and Adobe Analytics: Adobe Commerce Cloud includes integrations with other Adobe Commerce Cloud products. This provides a full-featured digital commerce platform for both B2C and B2B. These integrations allow for deeper personalization and more sophisticated analytics across channels, enabling businesses to deliver a seamless and personalized customer experience.
Pricing of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, powered by Magento, operates on a subscription-based model. The cost is determined by your business’s annual Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) and Average Order Value (AOV). This means the more your business sells, the more you will pay for using Adobe Commerce.
There are several editions of Adobe Commerce:
Starter Edition: Priced at $20,000 per year, this edition is suitable for small businesses with basic requirements.
Professional Edition: Priced at approximately $40,000 per year, this edition includes B2B features and marketing automation tools.
If your business has specific needs or performs a significant amount of sales, the cost may be as low as $22,000 per year, but it can easily approach $100,000 per year.
In addition to the subscription cost, there are other costs associated with running an online store:
Domain: $10 to $20 per year
Web Hosting: $14.99 to $39.99 per month
SSL Certificate: $50 to $600 per year
Transaction Fees: Around 2% to 4% per transaction as credit card processing fees and payment platforms.
Please note that these are approximate costs and can vary based on your specific requirements and the service providers you choose.
For the most accurate and customized pricing, it’s recommended to contact Adobe directly. They can provide a quote tailored to your business’s specific needs and scale.
Role of Adobe Commerce in Digital Transformation
Adobe Commerce plays a significant role in digital transformation by serving as the focal point for businesses transitioning to a digital model. Here are some key points:
Central Role in Adobe Experience Cloud: Adobe Commerce is at the heart of the Adobe Experience Cloud. This strategic positioning allows Adobe to leverage its strengths in content and digital assets, marketing automation, and web experience to focus on the complete digital experience. This means that Adobe Commerce is not just a tool for managing transactions, but a comprehensive platform for managing all customer interactions across various touchpoints.
Modern and Composable Architecture: Adobe Commerce is built on a modern and composable architecture, which includes microservices, API-first, cloud-native, and headless approaches. This architecture provides the operational agility needed to meet emerging digital experience business needs and competitive pressure. It allows businesses to quickly adapt to changes in the market and customer behavior, and to integrate with other systems and services as needed.
Incremental Growth Along the Digital Maturity Curve: Adobe Commerce enables businesses to grow incrementally along the digital maturity curve. This means that businesses can start with basic digital commerce capabilities and gradually add more advanced features and functionalities as they become more digitally mature. This approach reduces the risk and complexity of digital transformation and allows businesses to learn and adapt as they go.
Integration with Adobe Experience Cloud: Adobe Commerce is integrated with the broader Adobe Experience Cloud application ecosystem. This integration allows businesses to leverage Adobe’s comprehensive suite of applications to enhance their digital commerce capabilities. For example, businesses can use Adobe Analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, Adobe Target to personalize customer experiences, and Adobe Campaign to manage marketing campaigns.
Support for Multiple Business Models: Adobe Commerce supports multiple business models. This means that it can be used by businesses of all types and sizes, from small online retailers to large multinational corporations. It also means that it can support various types of transactions, from simple one-time purchases to complex subscription and licensing models.
Composable Commerce Experiences: The latest release of Adobe Commerce focuses on composability and truly embraces this approach. This allows developers to leverage major updates to enable composable commerce experiences. Composable commerce is the use of components from different vendors that can be easily assembled and reassembled to meet changing business needs.
In a nutshell, Adobe Commerce is a powerful tool for digital transformation. It provides businesses with the flexibility, agility, and capabilities they need to succeed in the digital age.
How does Adobe Commerce Work?
Adobe Commerce, previously known as Magento, is a comprehensive commerce platform that was acquired by Adobe in 2018. It’s designed to be flexible, extensible, and scalable, making it a robust platform for managing e-commerce websites. It offers advanced data-sharing capabilities and artificial intelligence on a unified platform, which allows businesses to create end-to-end personalized experiences.
The platform uses AI to deliver personalized site searches, product recommendations, and browsing. This means that each customer can have a unique experience tailored to their preferences and behavior.
One of the key features of Adobe Commerce is its seamless integration with other systems. It can integrate into your existing ERM, CMS, and CRM tech stack. Moreover, it natively integrates with several key platforms, including Amazon. This allows users to manage their online marketplace presence alongside their e-commerce store, providing a unified and streamlined approach to online sales.
Data management is another area where Adobe Commerce shines. Its cloud-based functionality makes data management effortless. It uses a headless architecture, which means you can update all customer-facing data without disrupting the backend logistics. This is particularly useful for businesses that need to make frequent updates to their product listings, prices, or other customer-facing information.
Scalability is a crucial aspect of any e-commerce platform, and Adobe Commerce is built to grow your business. It supports multiple business models and simplifies complex commerce processes. This means that as your business grows and evolves, Adobe Commerce can adapt to meet your changing needs.
Finally, Adobe Commerce allows you to expand your commerce capabilities with thousands of free and premium apps and extensions. These can add new features to your store, integrate with other services, and generally enhance your e-commerce capabilities.
In summary, Adobe Commerce is a powerful commerce engine that provides a comprehensive solution for managing and scaling your e-commerce business. It offers a range of features and capabilities that can help you create a successful and efficient online store. Whether you’re a small business just starting or a large enterprise looking to streamline your online sales, Adobe Commerce has the tools and features to help you succeed.
How does Adobe Commerce Help Reach the Omnichannel Consumer?
Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento Commerce, provides a comprehensive solution to reach the omnichannel consumer. Here’s how:
Channel-Less Approach: Adobe Commerce ensures that your brand’s look, feel, and language are presented consistently across all channels and touchpoints. This approach helps in creating a cohesive omnichannel experience. It is about integrating multiple marketing channels in a way that affords the end user a seamless front-end experience.
Magento Order Management: This feature allows you to fulfill orders in the most efficient way for you and your customers. It ensures a smooth e-commerce experience, where customers can place an order through a brand’s e-commerce website, check the order status on their native mobile app, and even return an item at a physical store.
Magento Page Builder: This tool accelerates content creation and publishing, helping to build lasting relationships with diverse shopper personas. It enables you to create compelling storefront experiences.
Magento Business Intelligence: This feature provides easy analysis of customer data with pre-built and custom dashboards, revealing active customer trends and purchasing behaviors. It helps in promoting products based on shared data.
Magento Commerce API: This API helps synchronize online and in-store experiences by integrating your commerce platform with multiple point-of-sale (PoS) solutions. It ensures customers can interact with your brand across connected channels.
Front-end Flexibility: Adobe Commerce provides GraphQL APIs for flexibility to build any front-end experience and PWA Studio for creating high-performing PWAs optimized for Adobe Commerce’s back-end. It allows you to enable high-performing buying experience across mobile and desktop, and build commerce into new digital touchpoints.
Global Reach: With support for multiple languages, currencies, and tax rates, Adobe Commerce allows businesses to reach a global audience. It ensures a consistent customer experience regardless of the channel or device they prefer to use.
By leveraging these features, Adobe Commerce helps businesses deliver a seamless, omnichannel commerce experience that meets customers where they are and anticipates their needs.
What Level of Governance does Adobe Commerce Offer?
Adobe Commerce’s governance model is a comprehensive oversight function that is aligned with the organization’s structure and spans the entire project life cycle. It provides the project manager and team with a structured environment, processes, decision-making models, and tools that are essential for managing and controlling the project. This level of governance is particularly crucial for complex and strategic projects as it ensures their successful delivery.
The governance model of Adobe Commerce is about more than just defining and documenting effective practices. It also communicates these practices and provides a framework for making decisions. This framework helps in defining roles, responsibilities, and liabilities that are necessary for the successful completion of the project.
Another important aspect of Adobe Commerce’s governance model is its reporting and escalation structure. This structure extends from the execution team to the executive management. It defines the activities, reporting mechanisms, escalation procedures, and the flow of information. This ensures that there is periodic visibility at every level, which is crucial for the success of the project.
Lastly, Adobe Commerce’s governance model also emphasizes the importance of measuring project and quality performance Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), in addition to the sprint metrics. This comprehensive method of controlling the project and providing periodic visibility at every level is what makes Adobe Commerce’s governance model stand out. It is designed to ensure the success of the project.
Why do Large Companies Choose Adobe Commerce?
Adobe Commerce is equipped with a wide array of tools and functionalities that are essential for creating engaging web stores. It offers an intuitive drag-and-drop page builder, efficient inventory management, and the capability to provide a unified shopping experience across various channels. This means that companies can create a seamless and engaging shopping experience for their customers, regardless of the platform they choose to shop on.
In addition to providing the tools needed to create an engaging online store, Adobe Commerce also helps companies reach new audiences. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to expand their customer base and tap into new markets.
One of the standout features of Adobe Commerce is its strong and adaptable features, making it an ideal choice for B2B e-commerce companies. It boasts native B2B capability, open-source design, customization options, and simple backend system integrations. This means that it can be tailored to meet the specific needs of B2B companies, providing them with a platform that is both robust and flexible.
Lastly, Adobe Commerce leverages the benefits of modern cloud computing. It is built on a cloud-native and extensible architecture, which provides enterprise-grade scalability and availability. This allows it to deliver exceptional commerce experiences while supporting multiple brands, sites, currencies, and global regions. In other words, it provides the infrastructure needed to support large-scale e-commerce operations.
In summary, the combination of its comprehensive tools and functionalities, ability to reach new audiences, strong and adaptable features, and the benefits of cloud computing make Adobe Commerce a popular choice among large companies for their e-commerce needs. It provides them with a robust and flexible platform that can be tailored to meet their specific needs, while also providing the infrastructure needed to support large-scale e-commerce operations. This is why many large companies choose Adobe Commerce for their e-commerce needs.
How does Adobe Commerce Ensure Security for Its Users?
Adobe Commerce uses a comprehensive approach to security to ensure the safety of its users’ data and transactions. Here are some of its key features:
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This is a security measure that requires two forms of identification before a user can access their account. The first form is typically something the user knows, like a password. The second form is something the user has, like a mobile device. When a user tries to log in, they first enter their password. Then, a code is sent to their mobile device. The user must enter this code to complete the login process. This provides an additional layer of security because even if someone else knows the user’s password, they would also need access to the user’s mobile device to log in.
CAPTCHA and reCAPTCHA: CAPTCHA is a test used to determine whether the user is a human or a bot. It usually involves solving a puzzle or entering text from an image. reCAPTCHA is a more advanced version of CAPTCHA developed by Google. It uses an advanced risk analysis engine and adaptive challenges to keep malicious software from engaging in abusive activities on your site.
Security Scan: Adobe Commerce offers a Security Scan tool that continuously monitors sites for known security risks, malware, and unauthorized access. It provides real-time insights into the security status of the Adobe Commerce environment. If any security vulnerabilities are detected, the tool proactively notifies users so they can take immediate action.
Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Adobe Commerce supports strong encryption standards for data in transit (as it travels from one place to another) and at rest (when it is stored). This ensures that sensitive information like customer details and merchant data are protected from unauthorized access.
Regular Vulnerability Audits: Adobe Commerce regularly conducts vulnerability audits to identify and address potential security weaknesses within the platform. These audits involve a thorough examination of the system to identify any vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. Once identified, these vulnerabilities are addressed to strengthen the system’s security.
Education and Training: Adobe Commerce emphasizes the importance of education and training on security best practices. By educating users about potential threats and how to protect against them, Adobe Commerce fosters a culture of security awareness. This collective effort helps maintain a secure environment for conducting commerce.
These measures ensure a secure shopping experience for users and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches. However, users also have a responsibility to follow best practices to maintain the security of their own data and accounts.
History of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, which was formerly known as Magento Commerce, is a leading eCommerce platform. Adobe, a name that has been synonymous with creativity for many decades, is known for creating and publishing photos and graphics. In 2018, Adobe acquired Magento Commerce to integrate it with Adobe Experience Cloud, an Enterprise CMS platform by Adobe. This integration aimed to provide businesses with a comprehensive platform for creating and delivering effective digital experiences.
Adobe Commerce was initially released as Magento Commerce on April 11, 2016. In April 2021, Magento Commerce was rebranded to Adobe Commerce. This rebranding was part of a long-term project to integrate Magento within the Adobe Experience Cloud business unit.
Adobe Commerce is a collection of tools and technologies that combines the best of both brands, Magento and Adobe, into one platform. It is a top-notch B2C and B2B eCommerce platform and an efficient and easy-to-use CMS. Adobe Commerce offers advanced features that help businesses secure an edge over competitors, such as easy integration with backend systems, native B2B functionality, and personalization. It also accelerates the go-to-market time for businesses to help them deliver end-to-end omnichannel experiences. eCommerce platforms based on Adobe Commerce are highly scalable, robust, and deliver amazing performance.
Adobe Commerce Services
Adobe Commerce offers a variety of services to optimize and manage e-commerce operations. Here are some key services:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Adobe Commerce operates on a SaaS model, which means the software isn’t installed on-premises or maintained by the users themselves. Instead, your e-commerce system runs on Adobe’s hosted servers. Saas licensing models usually operate on a subscription basis, where users pay a monthly fee based on the level of service and the number of users.
Maintenance: One of the core advantages of a SaaS e-commerce platform like Adobe Commerce is maintenance. The provider is responsible for hosting and maintaining the software, uptime, performance, updates, and bug fixes. This allows the e-commerce or IT teams to focus on developing the code base of the online store while Adobe Commerce improves the infrastructure.
Security and PCI Compliance: Part of selling goods or services online is ensuring that the store meets PCI compliance standards so customer data, such as payment information, is safeguarded. In a SaaS e-commerce model, it’s the SaaS provider’s responsibility to stay up to date with patches and bug fixes that may impact the security of the store. Adobe Commerce is PCI-certified as a level 1 Solution Provider.
Scalability: Adobe Commerce is designed to meet the demands of mid-size and enterprise businesses, supporting large and complex catalogs, high transaction volumes, and global regions. With Adobe Commerce’s capability to horizontally scale both web and database tiers, customers can scale beyond the number shown: 208,000 orders per hour, 2 million pageviews per hour, 242 million effective SKUs, 10,500 GraphQL calls per minute, 500 concurrent back-office users.
Easy Integration: Adobe Commerce provides comprehensive storefront coverage that you can use to integrate with other storefronts, including Digital experience platforms (DXPs) like Adobe Experience Manager and Bloomreach, Content management systems (CMS) like Drupal and WordPress, and modern custom storefront applications like Adobe Commerce, PWA Studio, and Vue Storefront.
Adobe Managed Services: Adobe Managed Services provides hosted and managed applications and infrastructure for Adobe Commerce on cloud infrastructure Pro plans. It offers key benefits over on-premises and non-managed cloud implementations, including enhanced service level targets (SLTs), enhanced service level agreements (SLAs), and designated Cloud Expertise.
B2B Functionality: Adobe Commerce provides support for both B2B and B2C models. With the installation and enablement of the B2B extension in your Adobe Commerce store, the buying experience can be personalized with customer-specific catalogs and pricing and targeted content and promotions.
AI-Powered Commerce: Adobe Commerce’s AI capabilities are powered by Adobe Sensei, an integrated AI and machine learning framework. Adobe Sensei maximizes commerce data value and enhances decision-making.
Multi-Channel Commerce: Adobe Commerce powered by Magento is a single, multi-channel commerce platform with a unified back end and a flexible, customizable front end that lets you deliver exceptional customer experiences to every audience.
Personalized Commerce: Adobe Commerce enables customers to personalize the entire buying journey by sharing high-intent commerce data with other Adobe Experience Cloud solutions. AI-powered features in Adobe Commerce can help you quickly personalize your commerce experience and adopt personalization best practices.
In summary, personalized commerce in Adobe Commerce is about using AI and data to deliver a unique and tailored shopping experience to each customer, driving increased engagement and revenue.
Competitors of Adobe Commerce
Shopify
Shopify is a popular e-commerce platform known for its simplicity and ease of use. It’s a great choice for merchants who are launching an online business for the first time. With its simple interface and website builder, setting up an online store becomes a breeze. Shopify also offers a variety of sales and e-commerce functionalities and supports third-party digital tools. It’s a cost-effective solution, making it a go-to choice for entrepreneurs with a limited budget. Essentially, Shopify is ideal for small and medium-sized businesses that need a straightforward e-commerce solution.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento, is a robust e-commerce solution that offers more advanced features. It caters to businesses of all sizes and allows them to create multichannel experiences and deploy multiple multilingual websites. Adobe Commerce’s marketplace offers a wide range of native integrations for site optimization, customer support, marketing, shipping, and fulfillment. However, Adobe Commerce comes with a higher price tag, making it a better fit for medium and large businesses with larger budgets. It’s the right choice for companies that want to build unique branded experiences and add complex functionalities to their website.
In terms of user reviews, Shopify has a slightly higher rating than Adobe Commerce. Shopify has a rating of 4.5 stars based on 457 reviews, while Adobe Commerce has a rating of 4.2 stars based on 265 reviews.
In conclusion, both Shopify and Adobe Commerce have their strengths and cater to different types of businesses. Shopify, with its ease of use, is a good choice for smaller businesses. Adobe Commerce, with its advanced customization options, is better suited to larger businesses.

VTEX Commerce Platform
When it comes to user satisfaction and ease of use, VTEX has a higher user satisfaction rating of 4.7 out of 5 compared to Adobe Commerce’s rating of 4.2 out of 5. Users have found VTEX easier to use, set up, and administer than Adobe Commerce.
In terms of features, both platforms offer a wide range of functionalities including Shipping Management, Multi-Store, Activity Dashboard, Order Tracking, Customer Accounts, Cataloging/Categorization, Promotions Management, Returns Management, Reporting & Statistics, Multi-Channel Management, Loyalty Program, Multi-Channel Marketing, CRM, Website Management, Customizable Templates, Data Synchronization, Real Time Data, Templates, Email Marketing, Kitting, Content Management, Sales Orders, SEO Management, Multi-Currency, Inventory Management, Inventory Tracking, Drag & Drop, Campaign Management, Order Management, Mobile Access, API, Customizable Branding, Multi-Location, Shopping Cart, Electronic Payments, Credit Card Processing, Reviews Management, Data Security, Third Party Integrations, Discount Management, Alerts/Notifications, Purchase Order Management.
Adobe Commerce is praised for its modern, composable framework with powerful APIs and micro-services, and its high customizability. However, users have reported complex integrations with CRM and ERP systems. On the other hand, VTEX is generally well-received by users, but specific pros and cons are not mentioned in the search results.
When it comes to recommendations, 77% of Adobe Commerce users are likely to recommend the product, while 94% of VTEX users are likely to recommend it.

BigCommerce
Both BigCommerce and Adobe Commerce are well-regarded in the digital commerce market. When we look at the ratings, Adobe Commerce has a rating of 4.2 stars based on 265 reviews, while BigCommerce has a slightly higher rating of 4.3 stars with 148 reviews.
In terms of capabilities, Adobe Commerce is recognized for its modern, composable framework that includes powerful APIs and micro-services. It’s highly customizable and adaptable, offering a great degree of flexibility. However, it does require technical knowledge and can be complex to integrate with CRM and ERP systems.
On the other hand, BigCommerce is an easy-to-use platform that businesses can use to build their online stores. It’s well-suited for small to large businesses.
If you’re looking for more flexibility and complete control over your e-commerce platform, Adobe Commerce could be a better option. But if you’re looking for an easy-to-use platform with everything you need to start your online store, BigCommerce could be a great choice.

SAP Commerce Cloud
Both BigCommerce and Adobe Commerce are well-regarded in the digital commerce market. When we look at the ratings, Adobe Commerce has a rating of 4.2 stars based on 265 reviews, while BigCommerce has a slightly higher rating of 4.3 stars with 148 reviews.
In terms of capabilities, Adobe Commerce is recognized for its modern, composable framework that includes powerful APIs and micro-services. It’s highly customizable and adaptable, offering a great degree of flexibility. However, it does require technical knowledge and can be complex to integrate with CRM and ERP systems.
On the other hand, BigCommerce is an easy-to-use platform that businesses can use to build their online stores. It’s well-suited for small to large businesses.
If you’re looking for more flexibility and complete control over your e-commerce platform, Adobe Commerce could be a better option. But if you’re looking for an easy-to-use platform with everything you need to start your online store, BigCommerce could be a great choice.

Spryker Cloud Commerce OS
Spryker Cloud Commerce OS is a commerce platform that caters to various sectors including B2B, Enterprise Marketplaces, D2C, and Thing Commerce. It’s developed with a focus on functionality and ease of use, thanks to its headless, API-first model. This allows businesses the flexibility to adapt, scale up, and achieve a quicker market entry. Spryker provides a system that supports businesses in their digital transformation journey by enabling them to realize value faster. It has a global presence and a diverse team, with a fully remote working culture. Spryker’s core model revolves around innovation, challenge, and solution-seeking. However, some users have mentioned that Spryker might not be the best choice for basic e-commerce needs but could be a good fit in a complex setup.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento Commerce, is a well-established platform in the e-commerce space. It offers a wide range of out-of-the-box features and extensive customization options. Adobe Commerce is known for its robustness and scalability, making it a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
In conclusion, the choice between Spryker Cloud Commerce OS and Adobe Commerce would depend on your specific needs and circumstances. If you need a flexible, innovative platform and have complex requirements, Spryker might be a good fit. On the other hand, if you prefer a platform with a wide range of built-in features and extensive customization options, Adobe Commerce could be a better choice.

Salesforce B2C Commerce Cloud
Adobe Commerce, previously known as Magento Commerce, is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that comes in two versions: an on-premise version and a cloud-hosted version. This open-source nature gives merchants full control over the platform and its features. It allows for both on-premise and cloud hosting and supports customization. Adobe Commerce supports multiple business models, including B2B and B2C selling, dropshipping, and more. Companies such as Nike, Helly Hansen, and Marie Claire rely on Adobe Commerce.
On the other hand, Salesforce Commerce Cloud is a Software-as-a-Service platform that caters to the needs of both large and medium-sized e-commerce businesses. As a SaaS platform, you’ll get limited access to the server and source code. It’s a ready-to-use service where the service provider takes care of servers, hosting, networks, and even cybersecurity. However, being a SaaS platform, it offers limited customization options. Salesforce Commerce Cloud is distributed in two versions to serve different industry models: Salesforce B2C Commerce and Salesforce B2B Commerce. Companies such as Adidas, GoPro, and Godiva rely on Salesforce Commerce Cloud.
The pricing for both platforms varies and depends on the specific versions and services you choose.

Oracle Commerce
When it comes to cloud e-commerce solutions, Oracle Commerce stands out with its true SaaS e-commerce solution. It offers frequent, automatic updates and maintenance, security enhancements, and autoscaling capabilities. Adobe Commerce Cloud, on the other hand, is cloud-hosted, and updates must be manually applied, which could potentially increase vulnerability to security threats.
In terms of implementation cost and speed, Oracle Commerce claims to offer faster implementations at a lower cost due to its robust native functionality. Adobe Commerce, however, relies on integration partners for core application support, which could increase costs and slow down implementation.
Oracle unifies data across CRM and back-office systems, allowing for real-time personalization across channels. Adobe Commerce provides rich analytics capabilities, but the incomplete integration with Magento may limit bidirectional data flow, impacting the system’s ability to use that data to personalize eCommerce experiences.
Oracle Commerce is built to handle any level of complexity, including B2B requirements, configurable products, and complex transactions. Adobe Commerce provides limited B2B eCommerce capabilities and relies on customizations and partners to complete their commerce solutions.
Users generally praise Oracle Commerce for its flexibility, customization options, and strong developer community, though some find the interface complex and the documentation lacking. Adobe Commerce is appreciated for its scalable architecture, omnichannel capabilities, and robust marketing automation.

Elastic Path Composable Commerce
Elastic Path Composable Commerce is a fully microservices-based headless commerce solution. This means that the front-end and back-end are decoupled, which allows for more flexibility in delivering unique front-end experiences without requiring extensive changes to the back-end. Elastic Path emphasizes on extensibility, which allows brands to tailor their commerce solution to their needs. According to Elastic Path, switching from a monolith or retrofitted headless solution like Magento to a composable commerce solution like Elastic Path can result in a roughly 50% reduction over three years in total cost of ownership. On Gartner Peer Insights, Elastic Path has a rating of 4.5 stars with 80 reviews.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce offers a headless solution, but it’s considered a retrofitted solution. This means that while it allows for more design freedom on the front-end, the back-end is essentially still a monolith, making changes or innovating fast can be difficult. Adobe Commerce has a rating of 4.2 stars with 263 reviews on Gartner Peer Insights. Some users have reported complex integrations with CRM and ERP systems.
In conclusion, both platforms offer robust eCommerce solutions, but they differ in their approach to headless commerce and extensibility. Elastic Path might be a better choice for brands looking for a fully decoupled, microservices-based solution, while Adobe Commerce might be more suitable for those who prefer a more traditional platform with a large population of experienced developers and SIs.

Shopware
Adobe Commerce and Shopware are both well-regarded in the digital commerce market. They each have their unique strengths and weaknesses, and the ideal choice really depends on your specific requirements.
Adobe Commerce has been rated 4.2 stars based on 263 reviews. Users appreciate its modern, composable framework which includes powerful APIs and micro-services. It’s highly customizable and adaptable, and its new headless framework enables the creation of lightning-fast eCommerce sites. However, it’s not without its challenges. Users have reported that integrating Adobe Commerce with CRM and ERP systems can be complex, and any changes can potentially lead to severe consequences, including integration failures.
On the other hand, Shopware also has an overall rating of 4.2 stars, but this is based on 68 reviews. Unfortunately, the specific strengths and weaknesses of Shopware weren’t mentioned in the search results.

Drupal Commerce
Drupal Commerce is a free, open-source content management system that is highly extensible and flexible. It’s particularly well-suited for organizations that need a robust content management system in addition to e-commerce capabilities. It offers core features such as account and menu management, RSS feeds, page layout customization, and system administration.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento, is an enterprise e-commerce software developed specifically for building e-commerce websites. It offers both free (open source) and proprietary licensing models. Adobe Commerce provides all the basic e-commerce capabilities and allows you to build a unique online store from the ground up. It supports very advanced eCommerce functionality that would otherwise be costly and difficult to implement.
When comparing the two, there are several key differences to consider. While both platforms are highly scalable, Drupal Commerce doesn’t organize products as effectively. In terms of content management, Drupal has robust capabilities, while Adobe Commerce has limited functionality. Adobe Commerce includes hosting, which Drupal does not offer. In terms of cost, Drupal is free and open-source, while Adobe Commerce pricing is based on annual Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) and Average Order Value (AOV).
In conclusion, if your organization is focused on having a powerful e-commerce platform and is less worried about publishing media content, Adobe Commerce might be a better choice. However, if you require a robust content management system in addition to e-commerce capabilities, Drupal Commerce could be a more suitable option.

WooCommerce
WooCommerce and Adobe Commerce are both popular e-commerce platforms, but they cater to different needs. WooCommerce is a plugin for WordPress, which makes it a good choice if you’re already using WordPress and want to add e-commerce functionality to your site. It’s known for its seamless integration with WordPress and its vast library of plugins and extensions, which allow you to extend the functionality of your online store.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce, formerly known as Magento, is a standalone product. It’s designed for businesses of all sizes and offers a wide range of features and customization options to create a seamless online shopping experience. One of its key strengths is its scalability, meaning it can adapt to your needs as your business grows.
Both platforms are open-source products, meaning that the original code is freely available for anyone to modify or build on to create a customized product. However, it’s worth noting that with Adobe Commerce, unless you’re willing to pay a high price or use a hosting provider with one-click installs, you’ll need a good understanding of command-line installation and coding to get the platform up and running.
In terms of setup and use, WooCommerce can be easily installed with a few clicks, especially if you’re already using WordPress. Adobe Commerce, on the other hand, may require a more technical understanding.

PrestaShop
When it comes to pricing, PrestaShop is generally considered to be more affordable than Adobe Commerce. However, affordability doesn’t mean a compromise on user-friendliness. PrestaShop is known for its user-friendly interface, although it does require some level of coding experience for customization.
Both PrestaShop and Adobe Commerce are highly flexible and scalable, catering to a variety of business needs. However, their target markets differ slightly. PrestaShop is often the go-to choice for smaller businesses, while Adobe Commerce is typically preferred by larger to enterprise-level businesses.
In terms of features, both platforms are quite robust. PrestaShop offers features like SEO optimization, a wide selection of modules and themes, an intuitive interface, and various marketing tools. On the other hand, Adobe Commerce provides features like multi-store management, multilingual support, a comprehensive toolset, and extensive customization options.
Lastly, if we look at the ratings, both platforms are quite closely matched. PrestaShop has a rating of 4.33 out of 5 stars based on 306 reviews, while Adobe Commerce has a rating of 4.31 out of 5 stars based on 623 reviews.

Rithum
Rithum and Adobe Commerce are both significant players in the e-commerce solutions market. Rithum was founded in 1997 and is a private company based in Atlanta, US. It provides technology automation, e-commerce, enterprise software, and marketing analytics platform and has around 1,132 employees. On social media, Rithum has around 2.2k Twitter followers.
On the other hand, Adobe Commerce was founded in 2008 and is a subsidiary based in San Jose, US. It provides technology cloud, e-commerce, enterprise software, and marketplace platform and has around 588 employees. Unlike Rithum, Adobe Commerce does not have a Twitter account.

Kibo Commerce
Kibo Commerce and Adobe Commerce are both powerful e-commerce platforms, each with its own unique features. Kibo Commerce is a headless SaaS platform that helps online businesses deliver personalized shopper experiences across various sales and fulfillment channels. It offers features like product information and distributed order management, AI-driven personalizations, merchandising, cart management, and analytics. On the other hand, Adobe Commerce is a flexible end-to-end platform that helps businesses digitize and personalize complex commerce processes throughout the customer journey. It supports multiple business models, including B2B and B2C selling, dropshipping, and more.
When it comes to their key differentiators and advantages, Kibo Commerce provides operational visibility by managing multiple brands, websites, sales channels, and region-specific fulfillment centers from a centralized dashboard. It also offers intelligent suggestions and recommendations to personalize every shopper’s experience. Adobe Commerce, however, provides a platform to manage, personalize, and optimize the commerce experience across every touch point and the customer journey.
As for pricing, the details for both platforms are not readily available and you may need to contact the sales team for detailed pricing. In terms of ratings, on a scale of 10, Kibo eCommerce scored 7.3 and Adobe Commerce (Magento Commerce) scored 7.8.

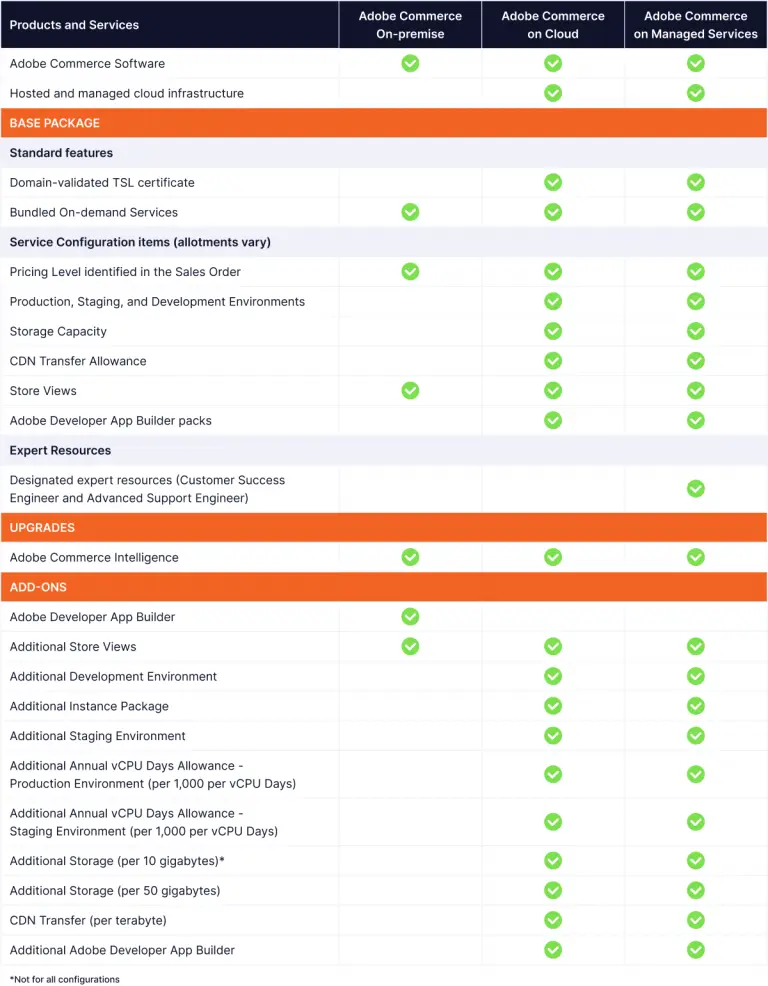
Architecture of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce, previously known as Magento Commerce, offers two plans: Starter and Pro. Each plan has a unique architecture designed to support your Adobe Commerce development and deployment process.
Starter Plan: This plan supports all Adobe Commerce features, including PayPal Onboarding Tool, and Commerce Reporting. It provides continuous cloud integration tools with unlimited users and includes Fastly Content Delivery Network (CDN), Image Optimization (IO), and added security with generous bandwidth allowances. New Relic APM (Performance Monitoring) is available on 3 branches: master and 2 of your choice. It offers Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) production, staging, and development environments (4 total active environments) optimized for Adobe Commerce. Egress filtering (outbound firewall) is available. It also provides 24×7 email support and monitoring for the core application and the cloud infrastructure.
Pro Plan: In addition to the features of the Starter plan, the Pro plan offers New Relic Infrastructure on Production + APM (Performance Monitoring) on staging and production. It provides Platform as a service (PaaS) based Integration development environments (2 total active environments) optimized for Adobe Commerce. It offers Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)—dedicated virtual infrastructure for Staging and Production environments. It has high-availability infrastructure and isolated and dedicated hardware in the underlying Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) to provide even higher levels of reliability and availability. It also provides a dedicated Customer Technical Advisor (CTA).
Both the Starter and Pro plan architectures deploy databases, web servers, and caching servers across multiple environments for end-to-end testing while supporting continuous integration. Adobe Commerce on cloud infrastructure uses a high-availability architecture that replicates each Pro project on three separate AWS or Azure Availability Zones, each zone with a separate data center.
Companies Using Adobe Commerce
Here are some companies that are using Adobe Commerce:
Food Service Direct, Inc.: They use Adobe Commerce to modernize their digital sales platform. This allows them to tailor their services to customer’s unique needs. They can expand their business into new service areas for both B2B and B2C customers.
HP: HP uses Adobe Commerce to deliver localized e-commerce experiences in countries throughout the Asia-Pacific region. They have also launched an “online-to-offline” sales effort to increase foot traffic in their brick-and-mortar (offline) stores.
Infosys Ltd: Infosys collaborates with Adobe to deliver remarkable customer experiences powered by Adobe Commerce. They focus on digital experience, commerce, and insights, enabling clients to navigate large-scale digital transformation programs powered by Adobe technology.
eBay Inc.: eBay uses Adobe Commerce to facilitate online consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer sales. It allows eBay to sell products in domestic or international markets easily.
Wipro Ltd: Wipro collaborates with Adobe to create integrated marketing, commerce, analytics, and customer experience solutions. These solutions help businesses to better understand and win customers, increase wallet share, and differentiate through targeted, relevant, and consistent conversations across multiple devices and channels.
Use Cases of Adobe Commerce
Adobe Commerce is a flexible and modern platform that is used for various purposes in e-commerce. Here are some of its key use cases:
B2B E-commerce: Adobe Commerce is extensively used in B2B e-commerce. It offers a flexible and intelligent B2B e-commerce solution that allows businesses to sell products to other businesses through an online portal. It provides integrated B2B functionality that offers world-class B2B buying experiences with custom catalogs and pricing, personalized experiences, and self-service customer portals for easy account management and ordering. This includes all kinds of products, from software and furniture to clothing and cooking utensils.
Customer Experience: Adobe Commerce helps businesses provide a quality online commerce experience for their customers. It allows businesses to present complex product offerings in a friendly, approachable, and easy-to-understand way. Adobe Commerce enables businesses to create highly compelling content, deliver it across diverse media through smartphones, tablets, e-readers, and other devices, and then optimize it through systematic targeting and measurement.
Scalability: Adobe Commerce platforms are scalable. By adopting new technologies, businesses can expand accessibility across the globe, increasing their growth potential. Adobe Commerce is designed to meet the demands of mid-size and enterprise businesses, supporting large and complex catalogs, high transaction volumes, and global regions.
Profit Margins: With an e-commerce store, there’s no need for expenses like shop floor, warehouses, or staff hires. Lower overhead increases the potential for higher profits. Adobe’s net profit margin as of November 30, 2023, is 27.97%, and the current operating profit margin for Adobe as of November 30, 2023, is 30.26%.
Digital Presence: Adobe Commerce allows businesses to have a digital presence without the requirement for a physical business space. Adobe Commerce, powered by Magento is an all-in-one digital commerce solution that helps businesses orchestrate every step of the customer experience – from discovery to delivery, across multiple channels, so that they can make each interaction count.
Adobe Commerce Acquisitions
Adobe made a significant move in the commerce sector by acquiring Magento Commerce on May 21, 2018. This acquisition, which was completed for $1.68 billion, led to Magento Commerce becoming an integral part of Adobe Commerce. The integration of these platforms allowed for a seamless connection with the Adobe Experience Cloud.
The inclusion of Magento Commerce Cloud into Adobe’s offerings has expanded its ability to serve both B2B and B2C customers on a global scale. Magento’s platform combines digital commerce, order management, and predictive intelligence into a unified commerce platform. This strategic acquisition has not only helped Adobe complete its commerce loop but also marked its entry into the realm of Cloud Computing.
Today, Adobe Commerce, powered by Magento, provides a comprehensive eCommerce software solution that covers everything from catalog management to payment processing to order fulfillment. It empowers merchants to quickly build new site content, set up effective product recommendations, and integrate B2B and B2C solutions on the same platform. This has significantly enhanced the capabilities of Adobe in the commerce sector.
How does Adobe Commerce Ensure Security for Its Users?
Cloud Infrastructure
- Adobe Commerce operates on cloud infrastructure provided by either Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
- These cloud platforms serve as the foundation for hosting and managing Adobe Commerce instances.
- Resources are automatically allocated based on virtual compute usage, ensuring optimal performance and risk mitigation.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Within the cloud infrastructure, Adobe Commerce sets up a PaaS Integration environment.
- This environment facilitates seamless communication between various components, enabling efficient development, testing, and service integration.
Adobe Commerce Core Components
- PHP: The server-side scripting language used for dynamic web pages.
- MySQL (MariaDB): The relational database management system storing essential data.
- Redis: An in-memory data structure store for caching and session management.
- RabbitMQ: A message broker supporting asynchronous communication.
- Supported search engine technologies enhance product search capabilities.
Performance Tools
- New Relic: A suite of performance tools for monitoring, debugging, and managing applications and infrastructure.
- These tools collect and analyze data from Adobe Commerce projects, aiding in optimization.
Content Delivery Network (CDN), Web Application Firewall (WAF), and Image Optimization (IO)
Fastly CDN: Ensures efficient global content delivery by caching and distributing assets. Provides built-in protection against DDoS attacks.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Ensures PCI compliance by safeguarding against security threats. Protects against injection attacks and cross-site scripting.
Image Optimization (IO): Real-time image manipulation and optimization for faster delivery. Offloads image processing from servers, improving overall performance.
Microservices Architecture
- Adobe Commerce leverages SaaS-based microservices.
- These intelligent microservices enhance scalability, agility, and overall system performance.